This blog post is based on Exploring Information Security episode 256. Gemini created the first draft and a human edited it for publication.
Last month saw the disclosure of CVE-2025-55182, nicknamed React2Shell. It Boasts a rare CVSS score of 10.0. The vulnerability allows unauthenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) in the React Server Components (RSC) ecosystem.
As we enter 2026, the situation continues to escalate. What began as targeted state-sponsored activity has transformed into a high-volume, automated "exploit shotgun" campaign by global botnets.
The Technical Reality: Logic Abuse, Not Just a Bug
At its core, React2Shell is an unsafe deserialization flaw residing in the RSC "Flight" protocol. When a server processes a request for a Server Component, it parses a payload to reconstruct internal program structures. The vulnerable packages—specifically react-server-dom-webpack, parcel, and turbopack—fail to validate this incoming data.
How the vulnerability is exploited:
Promise Hijacking: Attackers craft a fake "Chunk" object with a custom
.then()method.Execution: When the Node.js server attempts to resolve this object as a Promise, it inadvertently executes the attacker's code.
Full Access: Because this occurs within the Node.js context, the attacker gains full access to the process, the filesystem, and sensitive environment variables like database credentials and API keys.
New Development: The "Exploit Shotgun" (RondoDox Botnet)
By late December 2025, the threat landscape shifted. The RondoDox botnet has operationalized React2Shell as a primary initial access vector. Using an automated "exploit shotgun" approach, RondoDox fires multiple exploits at servers to see which succeed, with researchers observing up to 150,000 daily exploit attempts.
Once a Next.js server is compromised, the botnet typically:
Deploys the
/nuts/boltsloader to purge the host of competing malware.Installs the
/nuts/poopcryptocurrency miner.Establishes persistence via Mirai-derived variants like
/nuts/x86to maintain a foothold even if the application is later restarted.
The Denial-of-Service Variant (CVE-2025-55184)
In addition to the RCE, researchers have identified CVE-2025-55184, a React Function Denial-of-Service flaw.7 By sending a crafted payload containing a cyclic promise reference, an attacker can force the Node.js runtime into infinite recursion.7 This freezes the server indefinitely and prevents it from yielding back to the event loop, effectively taking the application offline.7
A Vulnerable Ecosystem: Widespread Impact
The pervasiveness of this flaw cannot be overstated. A standard Next.js project created using create-next-app is exploitable in its default configuration.8 By the end of 2025, nearly 90,000 systems were still identified as vulnerable.
Furthermore, this crisis coincides with a volatile npm supply chain environment. The Shai-Hulud Worm, a self-replicating npm malware, recently compromised over 180 packages to steal GitHub secrets and drain millions in cryptocurrency. These events together highlight a dangerous trend of targeting developers and JavaScript-based infrastructure to bypass traditional security perimeters.
Your Action Plan: January 2026 Update
If your application was online and unpatched during December 2025, you must assume breach. Post-exploitation activity has already included reverse shells to Cobalt Strike servers and the harvesting of high-value AI credentials, such as OpenAI API keys and Kubernetes tokens.
Step 1: Identify Affected and Compromised Assets
The first priority is gaining visibility into your exposure. You cannot patch what you cannot find.
Manual Inventory: Navigate to your project's
node_modulesfolder and check forreact-server-dom-webpack,react-server-dom-parcel, orreact-server-dom-turbopack. Versions 19.0.0 through 19.2.0 are vulnerable.Automated Scanning: Use the open-source CLI tool
npx react2shell-guardornpx react2shell-scannerto detect vulnerable dependencies across local repositories, container images, and live URLs.Audit Web Logs: Search your server access logs for signs of active probing. Look for HTTP POST requests containing the
next-actionorrsc-action-idheaders. Filter for request bodies containing$@patterns or the string"status":"resolved_model".Detect Post-Exploitation: Hunt for suspicious processes spawned by Node.js, such as unexpected reconnaissance commands like
whoami,id,uname, or attempts to read/etc/passwd. Watch for unusual file writes to the/tmp/directory, such aspwned.txtor botnet-related binaries.Scan for Supply Chain Indicators: Search for files like
setup_bun.jsandbun_environment.js, which are leading indicators of a Shai-Hulud 2.0 infection in your build environment.
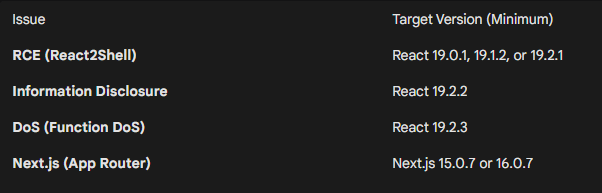
Step 2: Patch Immediately (Updated Versions)
Patching requirements have evolved to address both RCE and DoS variants:
Step 3: Rotate All Secrets
Successful exploitation grants access to environment variables. You must rotate all API keys (especially Cloud and AI providers), database credentials, and service tokens accessible to the vulnerable process.
Step 4: Audit for Persistence
Check for unauthorized files in /tmp, newly created users, or modified authorized_keys files. Monitor for suspicious outgoing connections to known botnet infrastructure.
Conclusion
React2Shell is the "Log4Shell of the Frontend." As we continue to move critical logic to the server, we must treat every deserialization boundary as a potential gateway for total compromise.
The React2Shell vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182) has fundamentally altered the threat profile of modern JavaScript web applications. As the "Log4Shell of the Frontend," it marks a paradigm shift where vulnerabilities previously restricted to the client side have moved directly to the server, granting unauthenticated attackers a "master-key" to total infrastructure compromise .
The speed of weaponization—with sophisticated China-nexus actors and industrialized botnets like RondoDox launching over 150,000 exploit attempts daily—underscores that patching is no longer a scheduled task but an emergency survival protocol . The simultaneous rise of the Shai-Hulud worm further emphasizes that the security of the modern web is only as strong as its deepest transitive dependency .
Remediation must go beyond simple code updates; it requires a comprehensive "assume breach" response, including the rotation of cloud and AI credentials and a forensic audit of CI/CD environments .
Resources
China-nexus cyber threat groups rapidly exploit React2Shell ... - AWS, accessed December 12, 2025, https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/china-nexus-cyber-threat-groups-rapidly-exploit-react2shell-vulnerability-cve-2025-55182/
How react2shell-guard Gives Devs a Practical Response Plan | by am | IT Security In Plain English | Dec, 2025, accessed December 12, 2025, https://medium.com/it-security-in-plain-english/how-react2shell-guard-gives-devs-a-practical-response-plan-5f86b98c44e4
CVE-2025-55182 – React Server Components RCE via Flight ..., accessed December 12, 2025, https://www.offsec.com/blog/cve-2025-55182/
Security Advisory: Critical RCE Vulnerabilities in React Server Components & Next.js - Snyk, accessed December 12, 2025, https://snyk.io/blog/security-advisory-critical-rce-vulnerabilities-react-server-components/
React2Shell flaw (CVE-2025-55182) exploited for remote code execution, accessed December 12, 2025, https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2025/12/11/react2shell-flaw-cve-2025-55182-exploited-for-remote-code-execution/
Detecting React2Shell: The maximum-severity RCE Vulnerability affecting React Server Components and Next.js | Sysdig, accessed December 12, 2025, https://www.sysdig.com/blog/detecting-react2shell
CVE-2025-55182 - CVE Record, accessed December 12, 2025, https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2025-55182
React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182): Critical React Vulnerability | Wiz Blog, accessed December 12, 2025, https://www.wiz.io/blog/critical-vulnerability-in-react-cve-2025-55182
React2Shell Security Bulletin | Vercel Knowledge Base, accessed December 12, 2025, https://vercel.com/react2shell
React2Shell and related RSC vulnerabilities threat brief: early ..., accessed December 12, 2025, https://blog.cloudflare.com/react2shell-rsc-vulnerabilities-exploitation-threat-brief/
CVE-2025-55182: React2Shell Analysis, Proof-of-Concept Chaos ..., accessed December 12, 2025, https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/25/l/CVE-2025-55182-analysis-poc-itw.html
React2Shell: Decoding CVE-2025-55182 – The Silent Threat in React Server Components, accessed December 12, 2025, https://blog.qualys.com/product-tech/2025/12/10/react2shell-decoding-cve-2025-55182-the-silent-threat-in-react-server-components
Serious React2Shell Vulnerabilities Require Immediate Attention, accessed December 12, 2025, https://www.sonatype.com/blog/react2shell-rce-vulnerabilities-require-immediate-attention
React2Shell and the Case for Deception in Your Vulnerability Management Program, accessed December 12, 2025, https://www.zscaler.com/blogs/product-insights/react2shell-and-case-deception-your-vulnerability-management-program